Scientific Large Model Research Group
Team Members
Introduction to Key Achievements
The emergence of scientific Large models has injected unprecedented momentum into complex scientific research. Their powerful computation and simulation capabilities are profoundly changing the way innovations occur across many fields—from drug design to materials development, from energy optimization to environmental management. By efficiently processing and analyzing vast amounts of data, these models accelerate research progress and open up new possibilities for tackling global challenges.
Representative Achievement 1: Collective Intelligence Model for Clinical Trials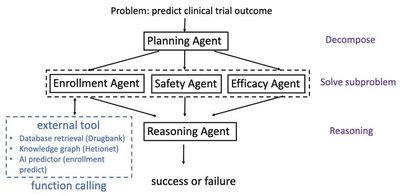
The integration of large language models and multi-agent systems has shown exceptional ability in natural language tasks such as text generation, semantic understanding, and logical reasoning. However, in the specialized and data-sensitive field of clinical trials, challenges remain—most notably limited access to external knowledge, which hinders the understanding and prediction of complex medical scenarios. To address this, we have developed an innovative ClinicalAgent platform based on a multi-agent architecture tailored for clinical trial tasks. By leveraging state-of-the-art techniques including GPT-4, the LEAST-TO-MOST strategy, and the ReAct reasoning framework, ClinicalAgent significantly improves performance in predicting clinical outcomes (with a PR-AUC improvement of 0.3326 over traditional methods) while unlocking new functionalities for handling complex challenges.
Relevant Publications:
Ling Yue, Sixue Xing, Jintai Chen, Tianfan Fu, ClinicalAgent: Clinical Trial Multi-Agent System with Large Language Model-based Reasoning, in Proceedings of the 15th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology and Health Informatics, 2024.
Representative Achievement 2: Collective Intelligence Model for Drug Repurposing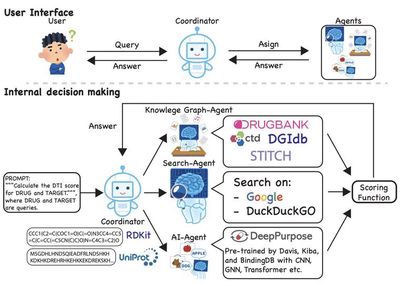
Drug repurposing offers a promising way to accelerate drug development by identifying new therapeutic uses for existing drugs—thereby shortening time-to-market, reducing costs, and lowering clinical trial risks. We propose an innovative multi-agent framework that integrates cutting-edge machine learning techniques and diverse data sources. The framework consists of three specialized agents: the AI Agent builds a robust Drug-Target Interaction (DTI) model; the Knowledge Graph Agent extracts DTI information from established databases such as DGIdb, DrugBank, CTD, and STITCH; and the Search Agent annotates and validates the predictions by interacting with a vast corpus of biomedical literature. This collaborative approach not only enhances the accuracy of drug-disease predictions but also provides interpretable insights fundamental for understanding the underlying mechanisms.
Relevant Publications:
Yoshitaka Inoue, Tianci Song, Tianfan Fu, DrugAgent: Explainable Drug Repurposing Agent with Large Language Model-based Reasoning, arXiv:2408.13378.
Representative Achievement 3: Automated Code Agent for AI-driven Drug Discovery
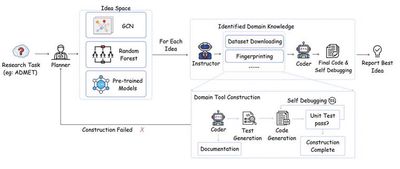
The rapid advancement of large language models has opened new avenues to accelerate drug discovery. Despite their potential, key challenges remain when translating theoretical concepts into practice in the highly specialized pharmaceutical domain. To overcome these obstacles, we introduce DrugAgent—a multi-agent framework that automates machine learning programming for drug discovery. Integrating domain expertise and automated ML tasks, DrugAgent streamlines the process from data acquisition to performance evaluation. For example, using the PAMPA dataset for absorption prediction, a Random Forest model achieved an F1 score of 0.92, exemplifying its high predictive capability. This breakthrough not only addresses inefficiencies in traditional methods but also paves the way for AI-driven innovations in pharmaceutical research.
Relevant Publications:
Sizhe Liu, Yizhou Lu, Siyu Chen, Xiyang Hu, Jieyu Zhao, Tianfan Fu, Yue Zhao, DrugAgent: Automating AI-aided Drug Discovery Programming through LLM Multi-Agent Collaboration, arXiv:2411.15692